Food & Snack Sources of Vitamin A
Vitamin A is not actually a single compound but a group of fat-soluble molecules. The vitamin supports important physiological processes and is an essential part of a balanced diet. Choosing foods and snacks that contain vitamin A will help maintain these processes and help support your overall health.
What Does Vitamin A Do?
Vitamin A consists of several molecules within the retinoid class, including retinol, retinyl esters, and retinal (Office of Dietary Supplements, 2016). This vitamin is necessary to promote the health of skin, teeth, soft tissues, and mucus membranes (Wax, 2015). One of the most critical roles of vitamin A is to help form the compound rhodopsin. Rhodopsin is a protein found in the retinas of the eyes. It is important for vision, particularly in low light.
Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamin A
Vitamin A is one of four fat-soluble vitamins used by the human body (the others are D, E, and K). This means that the body stores excess vitamin A in fat deposits. Unlike water-soluble vitamins, which are simple excreted when found in excess, it is technically possible to overdose on vitamin A. In practice, this is highly unlikely among people following typical diet plans.
The units of vitamin A are typically listed as micrograms (mcg) of retinol activity equivalents, or RAEs. This is because different forms of vitamin A differ in their activity. All vitamin A sources are eventually metabolized into retinol, making this an easy way to assess daily intake.
Adult men need 900 mcg RAE per day, while women need 700 mcg RAE. During pregnancy, women should aim to get 770 mcg RAE. While breastfeeding, their need increases sharply; lactating women should try to get 1,300 mcg RAE per day.
Foods that Are Good Sources of Vitamin A
Fruits, vegetables, and other foods make good sources of vitamin A. Eating a varied and healthy diet will ensure you naturally get enough of this important nutrient. Some good sources of vitamin A include (Office of Dietary Supplements, 2016):
- Sweet potatoes (1,400 mcg RAE per sweet potato)
- Spinach (573 mcg RAE per ½ cup)
- Cantaloupe (135 mcg RAE per ½ cup)
- Beef liver (6,500 mcg RAE per 3 ounce serving)
- Carrots (459 mcg RAE per ½ cup)
- Black-eyed peas (66 mcg RAE per serving)
- Dried apricots (63 mcg RAE per 10 apricot halves)
- Broccoli (60 mcg RAE per ½ cup)
- Mangoes (112 mcg RAE per mango)
The type of vitamin A depends on whether the food is a plant or animal source. Animal sources primarily contain preformed vitamin A, while plant-based sources tend to have vitamin A precursors. Both of these forms are a good way to get vitamin A into your diet.
Best Ways to Ensure Vitamin A Absorption
Because vitamin A is fat soluble, it is best absorbed when taken with dietary fats. Some foods rich in vitamin A, such as beef liver, naturally contain fats. Alternatively, it can be helpful to eat vitamin A-rich foods with nuts, seeds, flaxseed oil, or olive oil.
Recipes Rich in Vitamin A
If you’re looking for meals or snacks that ensure you consume sufficient amounts of this essential nutrient then look no further than to our compilation of recipes below. Each of these delectable dishes offers a superb supply of the vitamin to help you meet your nutritional needs.
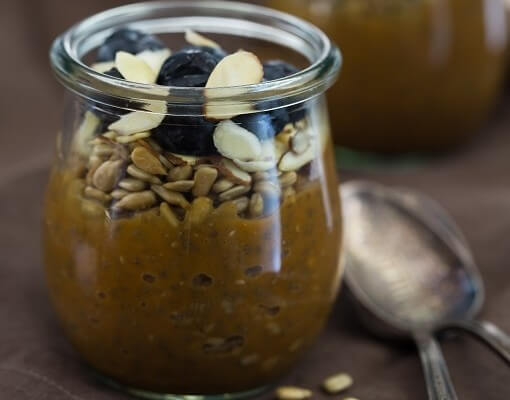

Pumpkin Chia Seed Pudding Recipe
Get a whopping 191% of the Daily Value (DV) for vitamin A before lunch with a serving of this palatable pumpkin pudding. The low-calorie meal is also rich in protein and fiber!
Ingredients: Milk, pumpkin puree, chia seeds, maple syrup, pumpkin spice, sunflower seeds, sliced almonds, fresh blueberries.
Total Time: 10 minutes
| Yield: 4 servings
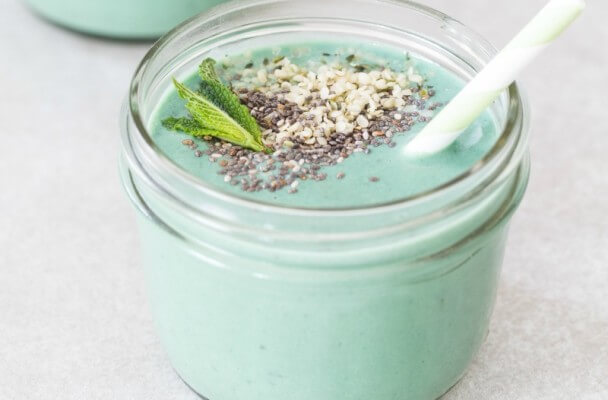

Protein-Packed Detox Smoothie Recipe {vegan}
This super smoothie is rich in vitamins and minerals, offering even more of the nutrient than our pudding with 150% of the DV for vitamin A in each serving! The smoothie also serves up iron, calcium, potassium, protein and fiber in abundance.
Ingredients: Almond milk, frozen banana, spirulina, hemp protein powder (optional), fresh mint, chia seeds, hemp hearts.
Total Time: 5 minutes
| Yield: 2 servings
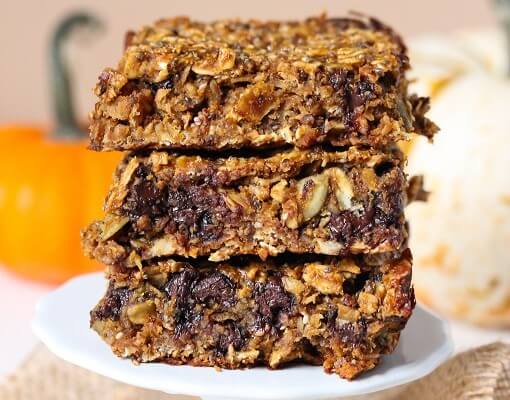

Pumpkin Granola Bars Recipe {gluten-free}
Another recipe that makes use of redolent, vitamin-rich pumpkin, these granola bars provide a perfect snack for anytime. Each bar also offers a hearty supply of iron, protein and fiber.
Ingredients: Gluten-free rolled oats, pumpkin puree, cashew butter, honey, maple syrup, dark chocolate chips, pumpkin seeds, chia seeds, pumpkin spice.
Total Time: 45 minutes
| Yield: 8 bars
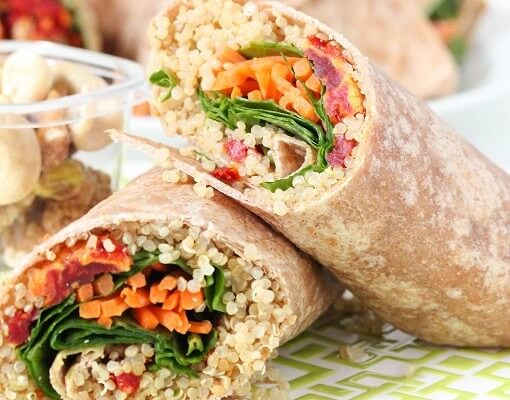

Quinoa Veggie Wrap Recipe {vegan}
Each of these simple vegan wraps contains 90% of the DV for vitamin A in addition to 11 grams of fiber and 13 grams of protein. Pack these palatable portions for a readily portable treat you can bring anywhere.
Ingredients: Tortilla wraps, quinoa, hummus, fresh spinach, sun-tomatoes, shredded carrots.
Total Time: 30 minutes
| Yield: 4 wraps

Farro Vegetable Salad Recipe
This scrumptious salad serves up a moderate amount of the vitamin, along with other essential vitamins and minerals. Add this delicious dish to your repository of recipes for a well-balanced delight that pairs with any plate!
Ingredients: Organic farro, sun dried tomatoes, frozen corn (thawed), scallions, black olives, feta cheese, cherry tomatoes, shredded carrots, salt, fresh dill, fresh mint, extra virgin olive oil, balsamic vinegar.
Total Time: 1 hour
| Yield: 6 servings
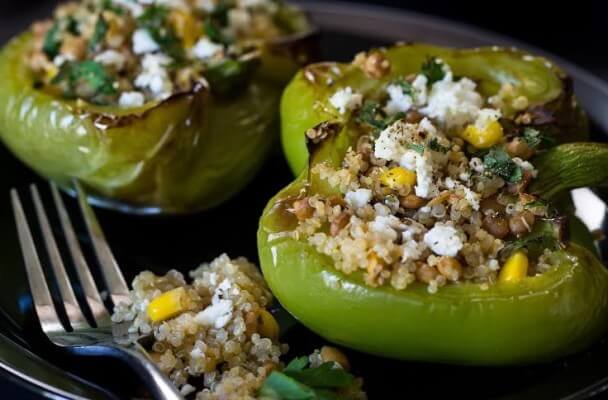

Quinoa Stuffed Peppers Recipe {gluten-free}
A perfect plate for supper, these peppers are packed with a plethora of wholesome ingredients, which together offer more than a third of the DV for vitamin A, 27 grams of fiber, and 30 grams of protein among other copious quantities of essential vitamins and vitamins.
Ingredients: Quinoa, green bell peppers, canned lentils, fresh spinach, feta cheese, frozen corn (thawed), salt, black pepper.
Total Time: 40 minutes
| Yield: 6 servings (8 half-peppers)
Snack Sources of Vitamin A
Searching for easy ways to add vitamin A to your diet with relatively little effort? Check out the suggestions below for snacks and ingredients that are packed with this needed nutrient.
Healthy Eating
- Healthy Highlights
- 5 Uses for Cacao Powder
- 5 Ways to Eat Farro
- 6 Best Gluten-Free Foods
- Alcohol and the Body
- Almond Flour Recipes
- Anti-Aging Superfoods
- Beat the Afternoon Slump
- Benefits of a Plant-Based Diet
- Benefits of Baobab
- Benefits of Cashews
- Benefits of Coconut Oil for Hair
- Benefits of Coconuts
- Benefits of Dates
- Benefits of Fenugreek
- Benefits of Garcinia Cambogia
- Benefits of Goji Berries
- Benefits of Kale Chips
- Benefits of Monk Fruit Sweetener
- Benefits of Peanuts
- Benefits of Pecans
- Benefits of Pistachios
- Benefits of Pumpkin Seeds
- Benefits of Spelt Flour
- Benefits of Steel Cut Oats
- Benefits of Sunflower Seeds
- Benefits of Tiger Nuts
- Benefits of Turmeric
- Benefits of Walnuts
- Benefits of Wheatgrass
- Best Food Fads
- Cacao vs Cocoa
- Caffeine-Free Energy Foods
- Chocolate That's Good for You
- Diet vs. Exercise
- Fat Burning Foods
- Food Myths Debunked
- Foods for Bone Density
- Foods for Colon Health
- Foods for Healthy Hair
- Foods for Healthy Skin
- Foods to Help Sleep
- Foods to Reduce Stress
- Green Tea Benefits
- Healthy Baking Flours
- Heart Healthy Habits
- High Protein Health Risks
- How to Boost Your Metabolism
- How to Lose Weight While Aging
- How to Throw a Vegan BBQ
- Kaniwa vs Quinoa
- Little Health Foods
- Low-Carb: Fad or Friend?
- Making Healthier Desserts
- Mediterranean Diet Meal Plan
- Natural Beauty Products
- Nuts for Weight Loss
- Preparing Vegan Meals
- Preventing Muscle Degeneration
- Rare Superfoods
- Reduce Sugar Intake
- Save Time By Going Vegan
- Smarter Snack Swaps
- Smoothie Ingredients
- Soy Protein vs Whey Protein
- Starting a Plant-Based Diet
- Steel Cut vs Rolled Oats
- Sugar Substitutes
- Vegan Proteins
- Vegan Substitutions for Fall Recipes
- Why Go Vegan
- Healthy Meals
- Healthy Recipes
- Sports Nutrition
- Nutrition and Special Diets
- 21 Day Fix
- 5 Popular Diet Similarities
- Alkaline Diet
- Anti-Inflammatory Diet
- Calorie Counting
- Carb Cycling Diet
- Celiac Disease
- Cholesterol
- Clean Eating
- Crohn's Disease
- DASH Diet
- Detox Diet
- Diabetes
- Diabetes Diet
- Diet Pill Dangers
- Fat Burning Foods
- Gluten-free Diet
- Glycemic Index
- Heart Health
- High Blood Pressure Diet
- High Fiber Foods
- How to Eat Healthy
- How to Lower Blood Pressure
- Hypertension
- IBS Diet
- Ketogenic Diet
- Liquid Diet
- Low GI Foods
- Low-Carb Diet and Foods
- Low-Fat High-Carb Diet
- Mediterranean Diet
- Mediterranean Diet Foods
- Military Diet
- Nutrition Labels Explained
- Paleo Diet
- Raw Food Diet
- Superfoods
- Sustainable Weight Loss
- Thrive Diet
- Vegan Diet
- Vegetarian Diet
- Weight Loss Shakes
- Whole30
- Vitamins, Minerals & Nutrients