Food & Snack Sources of Vitamin B12
Food provides the body with dozens of nutrients that it cannot create on its own. Vitamin B12 is one of these essential nutrients (WHFoods, 2014). Getting enough vitamin B12 from food and snack sources ensures that your body continues to effectively carry out metabolic processes.
What Is Vitamin B12?
There is no single thing called vitamin B; rather, this group of vitamins includes eight compounds that often coexist in the same foods (Medline Plus, n.d.). One of these vitamins, vitamin B12, also goes by the name cobalamin. Cobalamin has a unique chemical structure that is the most complex of any vitamin (Miller, 2014). Additionally, it is the only vitamin that contains a metal ion. This structure endows vitamin B12 with special properties that make it an essential for normal physiological functioning.
Physiological Role of Vitamin B12
Perhaps the most important role for vitamin B12 is in forming red blood cells. Vitamin B12 is critical for this process, forming part of a pathway needed for the production of hemoglobin (Office of Dietary Supplements, 2015). Hemoglobin is the component of red blood cells that binds to oxygen, allowing these cells to transport oxygen throughout the body.
Vitamin B12 also plays major roles in neurological functioning, DNA syntheses, and chemical reactions (Miller, 2014). For example, the vitamin is important for the metabolism of homocysteine. When homocysteine levels are too high, a person is at increased risk for cardiovascular disease (Gerhard & Duell, 1999). Thus, getting the recommended amount of vitamin B12 in the diet may be helpful in modulating cardiovascular risk.
Recommended Daily Allowance for Vitamin B12
The amount of vitamin B12 the body needs depends on age and other factors. The National Institutes of Health recommend the following intake of vitamin B12 (Office of Dietary Supplements, 2015):
- Men and women (14+ years old) need 2.4 micrograms of vitamin B12 per day (Office of Dietary Supplements, 2015). For most people, vitamin B12 can be easily obtained from food sources and absorbed. However, some older adults may have difficulty getting enough of this vitamin due to difficulty with absorption. Thus, eating foods fortified with vitamin B12 or taking a daily supplement may be appropriate for these individuals. Otherwise, for most, this nutrient can be easily obtained through food sources.
- Pregnant women need 2.6 micrograms of vitamin B12 daily.
- Breastfeeding women need 2.8 micrograms of vitamin B12 per day.
Dietary Sources of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 occurs naturally only in animal products (Miller, 2014). The following foods are good dietary sources of vitamin B12:
- Mussels: 20.4 micrograms per 3-ounce serving
- Clams: 84.1 micrograms per 3-ounce serving
- Crab: 9.8 micrograms per 3-ounce serving
- Lean beef: 6.9 micrograms per 3-ounce serving
- Mackerel: 16.1 micrograms per 3-ounce serving
- Skim milk: 0.9 micrograms per cup
- Turkey: 0.8 micrograms per 3-ounce serving
- Beef liver: 70.7 micrograms per 3-ounce serving
- Yogurt: 1.1 micrograms per cup
- Egg: 0.4 micrograms in one large egg
Although animal products are the only naturally occurring sources of vitamin B12, several types of foods are fortified with this vitamin to ensure that Americans get enough. For example, a typical fortified breakfast cereal contains 6 micrograms per serving.
Ensuring You Get Enough Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 deficiency is uncommon among healthy adults who eat a typical omnivorous diet. However, certain medical conditions make vitamin B12 deficiency more likely. For example, gastrointestinal conditions such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis make it difficult for the body to effectively absorb vitamin B12 (Office of Dietary Supplements, 2015). Furthermore, the body’s ability to absorb vitamin B12 grows worse with age, putting older adults at risk for deficiency.
Vitamin B12 deficiency is associated with anemia, fatigue, constipation, poor appetite, weakness, weight loss, and tingling in the hands or feet. In more severe cases, prolonged vitamin B12 deficiency may lead to neurological problems such as balance issues, memory loss, confusion, depression, or dementia.
It is particularly important for vegetarians and vegans to carefully monitor their vitamin B12 intake. Because cobalamin is only found in animal products, it is easy for individuals following these diets to become deficient (Office of Dietary Supplements, 2015). Vegetarians may obtain vitamin B12 from eggs and nonfat dairy products. Vegans should check the labels of breakfast cereals, soy products, and plant milks, as these are often fortified with vitamin B12.
Recipes Containing Vitamin B12
These delectable recipes offer meals for anytime of day that add to your cobalamin intake. Because these recipes rely on natural sources of the nutrient, they are not vegan- although they do accommodate less strict vegetarian diets.
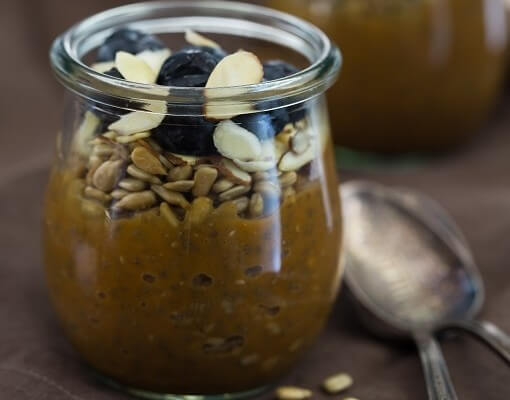

Pumpkin Chia Seed Pudding Recipe
This palatable pudding recipe allows you to add whichever milk you prefer. Opt for a reduced fat variety of dairy milk to add 1.3 micrograms of cobalamins per cup, which accounts for 21% of the Daily Value (DV) of vitamin B12 (U.S. Food and Drug Administration [FDA], 2015; United States Department of Agriculture [USDA], n.d.).
Ingredients: Milk, pumpkin puree, chia seeds, maple syrup, pumpkin spice, sunflower seeds, sliced almonds, fresh blueberries.
Total Time: 10 minutes
| Yield: 4 servings
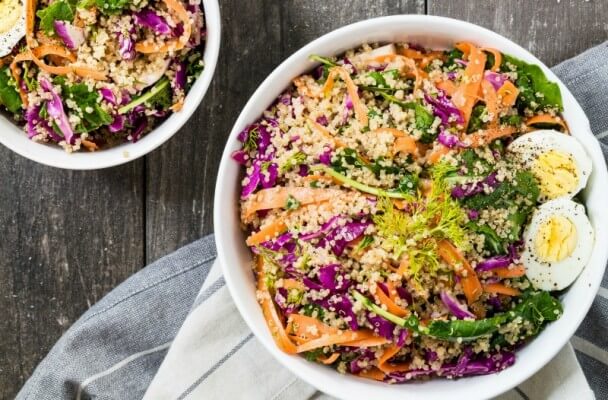

Kale Quinoa Salad Recipe
A large egg, when boiled, offers 0.56 micrograms or roughly 9% of the DV for the vitamin. It can be easily added to salads to increase both the vitamin B12 content of a food and its offering of protein, selenium, and iodine (FDA, 2015; USDA, n.d.). The salad is also packed with various nutrients from superfoods kale and quinoa.
Ingredients: Quinoa, fresh baby kale, purple cabbage, carrots, fresh dill, boiled eggs, rice wine, extra virgin olive oil, black pepper.
Total Time: 25 minutes
| Yield: 8 servings

Farro Vegetable Salad Recipe
According to the USDA (n.d.), An ounce of feta cheese supplies about 0.5 micrograms of vitamin B12, so adding cheese to your salad is a simple way of increasing your intake of the nutrient. The cheese also serves to add a full, creamy sensation to the palate of the dish that complements the tangy tastes and soft textures of the plate.
Ingredients: Organic farro, sun dried tomatoes, frozen corn (thawed), scallions, black olives, feta cheese, cherry tomatoes, shredded carrots, salt, fresh dill, fresh mint, extra virgin olive oil, balsamic vinegar.
Total Time: 1 hour
| Yield: 6 servings
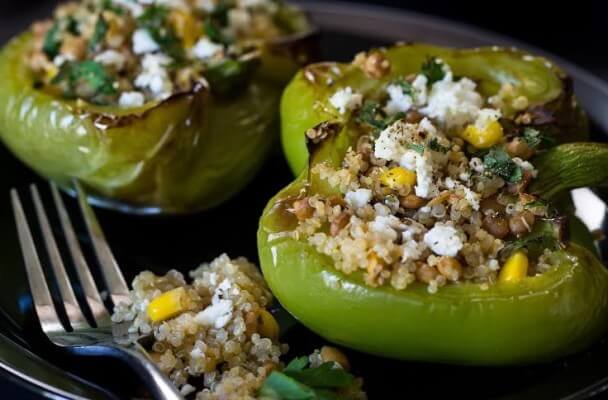

Quinoa Stuffed Peppers Recipe {gluten-free}
Another dish that utilizes feta cheese to add the nutrient to your diet, these stuffed peppers are also packed with quinoa, lentils, and spinach to supply a wholesome dish that is fit for lunch, dinner, or hearty appetizers at a dinner party. Each pepper is packed not only with vitamins and minerals, but it also contains plenty of protein and fiber.
Ingredients: Quinoa, green bell peppers, canned lentils, fresh spinach, feta cheese, frozen corn (thawed), salt, black pepper.
Total Time: 40 minutes
| Yield: 6 servings (8 half-peppers)
Additional Sources of Vitamin B12
The following snacks and ingredients offer a delicious means of adding cobalamins to your diet. Find simple treats to fit into almost any diet with these natural and fortified sources of the vitamin.
Healthy Eating
- Healthy Highlights
- 5 Uses for Cacao Powder
- 5 Ways to Eat Farro
- 6 Best Gluten-Free Foods
- Alcohol and the Body
- Almond Flour Recipes
- Anti-Aging Superfoods
- Beat the Afternoon Slump
- Benefits of a Plant-Based Diet
- Benefits of Baobab
- Benefits of Cashews
- Benefits of Coconut Oil for Hair
- Benefits of Coconuts
- Benefits of Dates
- Benefits of Fenugreek
- Benefits of Garcinia Cambogia
- Benefits of Goji Berries
- Benefits of Kale Chips
- Benefits of Monk Fruit Sweetener
- Benefits of Peanuts
- Benefits of Pecans
- Benefits of Pistachios
- Benefits of Pumpkin Seeds
- Benefits of Spelt Flour
- Benefits of Steel Cut Oats
- Benefits of Sunflower Seeds
- Benefits of Tiger Nuts
- Benefits of Turmeric
- Benefits of Walnuts
- Benefits of Wheatgrass
- Best Food Fads
- Cacao vs Cocoa
- Caffeine-Free Energy Foods
- Chocolate That's Good for You
- Diet vs. Exercise
- Fat Burning Foods
- Food Myths Debunked
- Foods for Bone Density
- Foods for Colon Health
- Foods for Healthy Hair
- Foods for Healthy Skin
- Foods to Help Sleep
- Foods to Reduce Stress
- Green Tea Benefits
- Healthy Baking Flours
- Heart Healthy Habits
- High Protein Health Risks
- How to Boost Your Metabolism
- How to Lose Weight While Aging
- How to Throw a Vegan BBQ
- Kaniwa vs Quinoa
- Little Health Foods
- Low-Carb: Fad or Friend?
- Making Healthier Desserts
- Mediterranean Diet Meal Plan
- Natural Beauty Products
- Nuts for Weight Loss
- Preparing Vegan Meals
- Preventing Muscle Degeneration
- Rare Superfoods
- Reduce Sugar Intake
- Save Time By Going Vegan
- Smarter Snack Swaps
- Smoothie Ingredients
- Soy Protein vs Whey Protein
- Starting a Plant-Based Diet
- Steel Cut vs Rolled Oats
- Sugar Substitutes
- Vegan Proteins
- Vegan Substitutions for Fall Recipes
- Why Go Vegan
- Healthy Meals
- Healthy Recipes
- Sports Nutrition
- Nutrition and Special Diets
- 21 Day Fix
- 5 Popular Diet Similarities
- Alkaline Diet
- Anti-Inflammatory Diet
- Calorie Counting
- Carb Cycling Diet
- Celiac Disease
- Cholesterol
- Clean Eating
- Crohn's Disease
- DASH Diet
- Detox Diet
- Diabetes
- Diabetes Diet
- Diet Pill Dangers
- Fat Burning Foods
- Gluten-free Diet
- Glycemic Index
- Heart Health
- High Blood Pressure Diet
- High Fiber Foods
- How to Eat Healthy
- How to Lower Blood Pressure
- Hypertension
- IBS Diet
- Ketogenic Diet
- Liquid Diet
- Low GI Foods
- Low-Carb Diet and Foods
- Low-Fat High-Carb Diet
- Mediterranean Diet
- Mediterranean Diet Foods
- Military Diet
- Nutrition Labels Explained
- Paleo Diet
- Raw Food Diet
- Superfoods
- Sustainable Weight Loss
- Thrive Diet
- Vegan Diet
- Vegetarian Diet
- Weight Loss Shakes
- Whole30
- Vitamins, Minerals & Nutrients