A Complete Guide to Protein Shakes for Muscle Building and Weight Loss
Once unique to the diet of bodybuilders, protein shakes are seeing increased inclusion in the diets of nearly anyone seeking to improve their health.
These shakes can be purchased pre-made, quickly created by combining protein powder with a preferred liquid, or carefully crafted with additional ingredients to produce a scrumptious protein smoothie.
But what kinds of benefits do protein shakes really offer, and do they really offer any advantage to eating protein-rich whole foods?
The Benefits of Protein Shakes
Potential benefits of protein shakes include: weight gain, the maximization of muscle muscle, and weight loss.
These purposes may confound at first, but the unique composition of the shakes can help to meet a variety of goals. Traditionally, these drinks are consumed by bodybuilders and athletes post-workout to facilitate the repair and growth of muscular tissue or to meet weight gain goals with extra, protein-rich calories.
In these instances, the shakes are consumed in addition to the standard diets of the weightlifters. However, the shakes can also provide a simple means of curbing appetite and providing essential nutrients without all the extra calories of a full meal, resulting in an overall caloric deficit for those that care to pursue slimmer waistlines (Zelman, 2014).
In addition to aiding weight loss when used appropriately, the shakes can provide benefits as simple as saving money. Protein shakes can be relatively inexpensive to make compared to alternative meal choices and are easy to make relative to recipes for more traditional meals.
Though there are certainly ample advantages to adding protein shakes to nearly any diet, it's essential to use them in a manner compatible with your specific goals (Virgin, 2015). So, how does the usage of shakes differ from person to person?
The answer is simple: the composition of each shake and the timing of your consumption relative to the rest of your diet and exercise regime will change depending on whether you want to add lean mass or shed body fat.
Primary Diet Roles for Protein Shakes

When people use protein shakes there are two main dietary roles. For those seeking to lose weight, the shakes need to act as a substitute for meals as opposed to an additional component. Additionally, those seeking to lose weight should ensure that their beverage consists of more than 50% protein. This is essential, as shakes and smoothies that supply more carbohydrates than protein may actually further facilitate weight gain (Zeratsky, 2015).
Those that do intend to use the shakes to gain weight will find themselves seeking similar shakes. Protein-packed collations are essential to building muscle, but should be paired with a complete and balanced diet for optimal efficacy.
This may entail adding additional nutrients to your drink or simply ingesting standard protein shakes in conjunction with an otherwise average, healthy diet. Lastly, endurance athletes seeking to refuel may opt for a beverage containing more fats and complex carbohydrates (Zelman, 2014).
Different types of protein
There are a number of different types of protein, and selecting the right variety may prove essential to success (VIrgin, 2015).
Whey Protein
Whey protein powder is the most common type in use today. It is a milk protein that is relatively inexpensive, effective, and widely available, which is why so many people use it.
Hemp Protein
Hemp protein is plant based, and often found in organic forms. It's a popular choice for those who want a plant based source for their protein, and those who are taking care with the planet.
Casein Protein
Casein breaks down more slowly than some other types of proteins, over the course of several hours. It's an excellent choice for people who want to take protein right before they go to bed.
Soy Protein
Soy protein can be an excellent choice of protein for vegetarians, who may not have a lot of other choices.
Getting Protein from a Shake
Whether getting protein from a shake is better than getting protein from foods is a question that has been hotly debated. There are pros and cons to both options, and the choice comes down to what the individual prefers. By using a shake people can get more protein in fewer calories, which is beneficial for weight loss; but, there are other means of attaining adequate protein with solid foods that may be easier to sustain (Zeratsky, 2015).
Recommended Recipes
You may also wish to consider purchasing additional supplements that can be mixed in with your preferred protein powder to quickly add a bastion of both nutrition and flavor. For example, try adding cacao powder, stevia powder, or green tea powder. In fact, when it comes to more elaborate mixtures, there’s no end to the combinations of delectable drinks you can create. Here are two of our favorite means of utilizing our hemp protein powder to create delectable protein shakes.
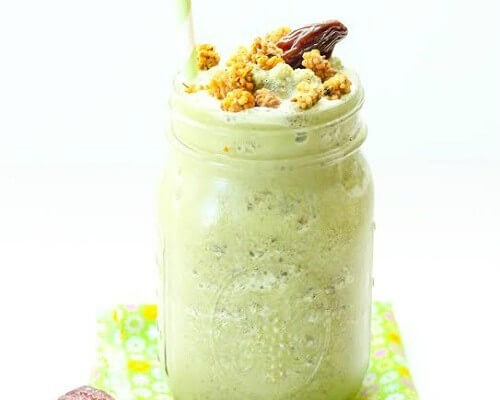

Matcha Green Tea Smoothie Recipe {gluten-free, vegan}
This gluten-free blend of matcha green tea, hemp, and almond powders offers a delectable drink that is sure to delight, and each serving supplies 10 grams of protein per serving.
Ingredients: Almond milk, matcha green tea powder, hemp protein powder, almond flour, dried mulberries, pitted dates, flaxseed meal, ice cubes, stevia powder.
Total Time: 5 minutes
| Yield: 4 smoothies
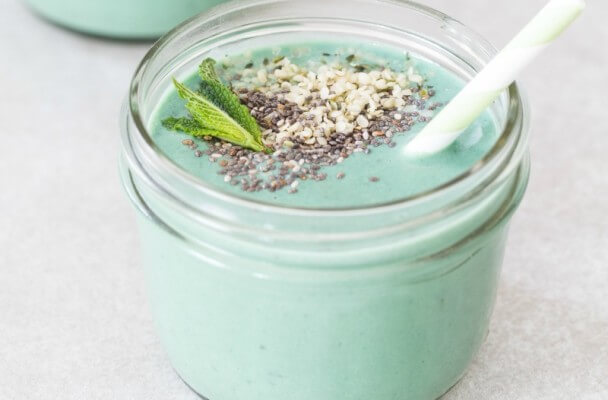

Protein-Packed Detox Smoothie Recipe {vegan}
A delectable detox drink, our spirulina protein smoothie offers a potent provision of protein from both hemp seeds and hemp powder with just under 20 grams per serving.
Ingredients: Almond milk, frozen banana, spirulina, hemp protein powder (optional), fresh mint, chia seeds, hemp hearts.
Total Time: 5 minutes
| Yield: 2 servings
Smoothie Additions
These items have a lot to offer for any protein smoothie you hope to make. In addition to our traditional protein powders listed above, these ingredients can be included in your blended beverages to add additional protein and other assorted nutrients to your diet without an excess of calories to go along with them.
For snacks that add to a protein-centered diet, check out our high-protein snacks page here.
Healthy Eating
- Healthy Snacks
- Healthy Highlights
- 5 Uses for Cacao Powder
- 5 Ways to Eat Farro
- 6 Best Gluten-Free Foods
- Alcohol and the Body
- Almond Flour Recipes
- Anti-Aging Superfoods
- Beat the Afternoon Slump
- Benefits of a Plant-Based Diet
- Benefits of Baobab
- Benefits of Cashews
- Benefits of Coconut Oil for Hair
- Benefits of Coconuts
- Benefits of Dates
- Benefits of Fenugreek
- Benefits of Garcinia Cambogia
- Benefits of Goji Berries
- Benefits of Kale Chips
- Benefits of Monk Fruit Sweetener
- Benefits of Peanuts
- Benefits of Pecans
- Benefits of Pistachios
- Benefits of Pumpkin Seeds
- Benefits of Spelt Flour
- Benefits of Steel Cut Oats
- Benefits of Sunflower Seeds
- Benefits of Tiger Nuts
- Benefits of Turmeric
- Benefits of Walnuts
- Benefits of Wheatgrass
- Best Food Fads
- Cacao vs Cocoa
- Caffeine-Free Energy Foods
- Chocolate That's Good for You
- Diet vs. Exercise
- Fat Burning Foods
- Food Myths Debunked
- Foods for Bone Density
- Foods for Colon Health
- Foods for Healthy Hair
- Foods for Healthy Skin
- Foods to Help Sleep
- Foods to Reduce Stress
- Green Tea Benefits
- Healthy Baking Flours
- Heart Healthy Habits
- High Protein Health Risks
- How to Boost Your Metabolism
- How to Lose Weight While Aging
- How to Throw a Vegan BBQ
- Kaniwa vs Quinoa
- Little Health Foods
- Low-Carb: Fad or Friend?
- Making Healthier Desserts
- Mediterranean Diet Meal Plan
- Natural Beauty Products
- Nuts for Weight Loss
- Preparing Vegan Meals
- Preventing Muscle Degeneration
- Rare Superfoods
- Reduce Sugar Intake
- Save Time By Going Vegan
- Smarter Snack Swaps
- Smoothie Ingredients
- Soy Protein vs Whey Protein
- Starting a Plant-Based Diet
- Steel Cut vs Rolled Oats
- Sugar Substitutes
- Vegan Proteins
- Vegan Substitutions for Fall Recipes
- Why Go Vegan
- Healthy Meals
- Healthy Recipes
- Nutrition and Special Diets
- 21 Day Fix
- 5 Popular Diet Similarities
- Alkaline Diet
- Anti-Inflammatory Diet
- Calorie Counting
- Carb Cycling Diet
- Celiac Disease
- Cholesterol
- Clean Eating
- Crohn's Disease
- DASH Diet
- Detox Diet
- Diabetes
- Diabetes Diet
- Diet Pill Dangers
- Fat Burning Foods
- Gluten-free Diet
- Glycemic Index
- Heart Health
- High Blood Pressure Diet
- High Fiber Foods
- How to Eat Healthy
- How to Lower Blood Pressure
- Hypertension
- IBS Diet
- Ketogenic Diet
- Liquid Diet
- Low GI Foods
- Low-Carb Diet and Foods
- Low-Fat High-Carb Diet
- Mediterranean Diet
- Mediterranean Diet Foods
- Military Diet
- Nutrition Labels Explained
- Paleo Diet
- Raw Food Diet
- Superfoods
- Sustainable Weight Loss
- Thrive Diet
- Vegan Diet
- Vegetarian Diet
- Weight Loss Shakes
- Whole30
- Vitamins, Minerals & Nutrients