Healthy Snacks for Football Teams
Whether juvenile football players are running the field or defending the other players, their bodies and minds must remain well-nourished and ready to perform at the limits. Although training exercises build muscle, improve coordination and increase speed, young football players often start to lose steam without an excellent diet. Healthy snacks mitigate the physiological demands of the sport by facilitating muscle fiber healing and restoring expended energy (Hoffman, 2015).
The Nutrition Game
So, what defines the ideal snack for football players? Athletes in general need plenty of energy, and the intensity of football can also place serious wear on muscles and the systems that maintain them. As such, it’s vital that the nutritional content of their collations matches these needs to supply plenty of protein and carbohydrates and to replenish the minerals and vitamins that support their growth and repair.
Plant-based, protein-rich snacks help athletes heal from microscopic muscle tears that occur while working hard on the football field. Over the course of the day, the dietary nutrient balance should include about 15 - 20% protein for kids up to age 18 (Webb, 2010). Additionally, many plant-based, protein-rich foods provide iron, which helps support adequate bone health. This support is of particular importance during the many growth spurt periods of adolescence and the teen years (Office of the Surgeon General (US), 2004).
When it comes to energy gains, carbohydrate rich foods provide the most bang for their caloric buck (Purcell, 2013). Complex carbohydrates are ideal for endurance sports, but natural sugars can help ramp up energy amidst an intense practice or between plays in an enduring game. Select sources of these sugars, such as fresh fruits, can also add much needed vitamins and minerals to their diet.
Vitamins & Minerals
Athletes need a wide variety of vitamins and minerals and definitely it’s best to get what your body needs from food first!
Consider foods that are rich in potassium and magnesium; and, generally speaking, atheletes don't need to skimp on the sodium due to fluid loss from sweat. Over time, sodium depletion can lead to muscle cramps, especially after a particularly grueling game or practice session (Kolata, 2008). Staying hydrated and arriving to games and practices hydrated is an important step in preventing muscle cramps.
There are several electrolytes that balance fluids in the body, including sodium and potassium. Adding potassium rich foods and consuming sodium can help to prevent concentration levels from dropping ot dangerous levels. For example, if potassium concentrations in the body drop to low levels, players may wake up in the middle of the night with painful cramps in their calves and thighs (Kolata, 2008).
Magnesium improves energy production by helping synthesize the building blocks of the metabolic process, adenosine triphosphate, or ATP (“Magnesium," 2005). As such, it’s important to pair this mineral with potassium, sodium, protein, carbohydrates, and plenty water. Pairing nuts with your choice of water or sports drink is one way to ensure an adequate intake of all of these nutrients; but, for additional ideas, we’ve included some additional snack suggestions and recipes in the sections below.
Recommended Recipes
It can be helpful to mix up your snack selection to prevent players from growing bored of the same old treats. Try these simple recipes to offer tasty confections that each supply the nutrients they need.
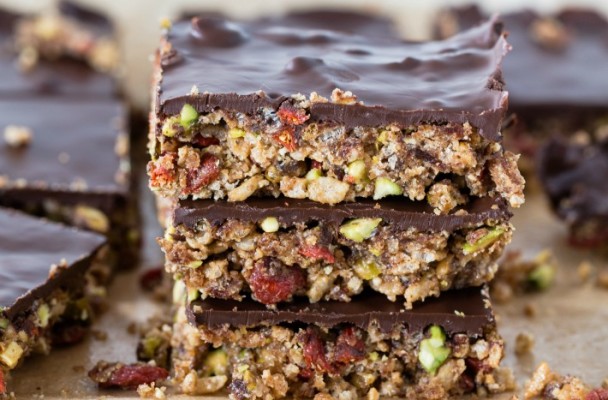

Chocolate Goji Berry Bars Recipe {gluten-free}
These bars combine the carbs of dates, quinoa puffs, and goji berries to supply a sudden burst of energy and an ample provision of the electrolytes to help maintain hydration to prevent muscle cramps.
Ingredients: Pitted dates, almond butter, quinoa puffs, goji berries, raw pistachios, coconut oil, dark chocolate chips.
Total Time: 20 minutes
| Yield: 8 bars
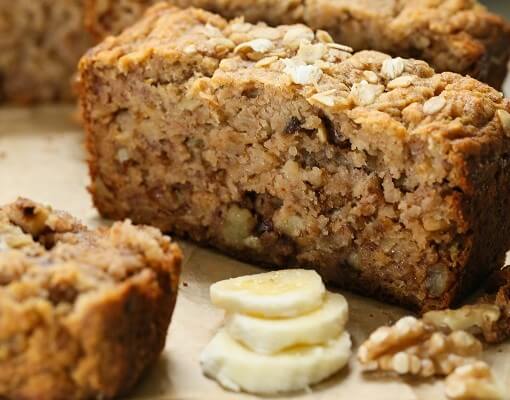

Banana Bread Recipe {gluten-free}
Bananas are a source of potassium, which plays a role in preventing muscle cramps. A loaf of this delectable dish also provides plenty of lasting energy in the form of gluten-free oats!
Ingredients: Overripe bananas, eggs, coconut oil, applesauce, almond milk, honey, vanilla extract, brown rice flour, coconut flour, walnuts, gluten-free rolled oats, baking soda, baking powder.
Total Time: 1 hour
| Yield: 12 servings
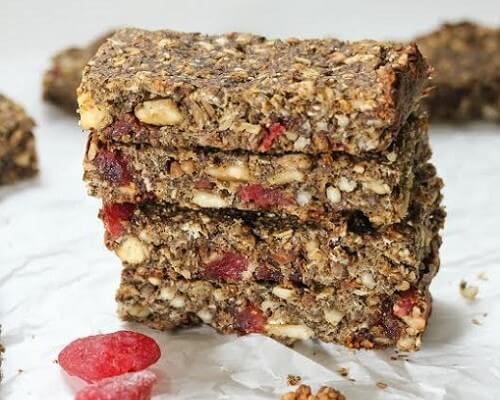

Homemade Granola Bars Recipe {gluten-free}
These crunchy confections are easy to stow away in a sports bag for a quick snack on the sidelines. This recipe is packed with fruits and oats for a supply of enduring energy and seeds and nuts to supply protein and other essential nutrients.
Ingredients: Dried mulberries, dried strawberries, raw cashews, organic peanut butter, ripe bananas, raw sunflower seeds, hemp protein powder, gluten-free rolled oats, chia seeds, flaxseed meal.
Total Time: 40 minutes
| Yield: 12 bars
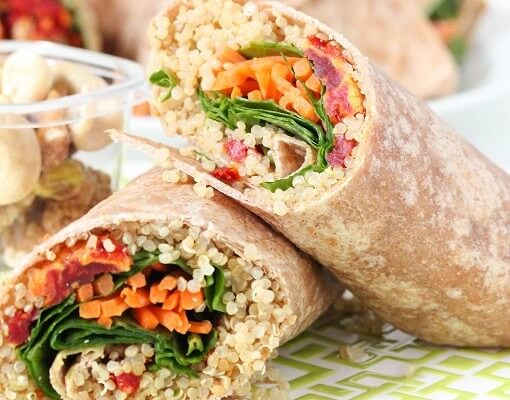

Quinoa Veggie Wrap Recipe {vegan}
These scrumptious snacks are balanced to provide not only plenty of protein, carbs, potassium, sodium, and magnesium- but also an abundance of other essential nutrients to support overall wellbeing.
Ingredients: Tortilla wraps, quinoa, hummus, fresh spinach, sun-tomatoes, shredded carrots.
Total Time: 30 minutes
| Yield: 4 wraps
Recommended Recipes
It can be helpful to mix up your snack selection to prevent players from growing bored of the same old treats. Try these simple recipes to offer tasty confections that each supply the nutrients they need.
Healthy Eating
- Healthy Highlights
- 5 Uses for Cacao Powder
- 5 Ways to Eat Farro
- 6 Best Gluten-Free Foods
- Alcohol and the Body
- Almond Flour Recipes
- Anti-Aging Superfoods
- Beat the Afternoon Slump
- Benefits of a Plant-Based Diet
- Benefits of Baobab
- Benefits of Cashews
- Benefits of Coconut Oil for Hair
- Benefits of Coconuts
- Benefits of Dates
- Benefits of Fenugreek
- Benefits of Garcinia Cambogia
- Benefits of Goji Berries
- Benefits of Kale Chips
- Benefits of Monk Fruit Sweetener
- Benefits of Peanuts
- Benefits of Pecans
- Benefits of Pistachios
- Benefits of Pumpkin Seeds
- Benefits of Spelt Flour
- Benefits of Steel Cut Oats
- Benefits of Sunflower Seeds
- Benefits of Tiger Nuts
- Benefits of Turmeric
- Benefits of Walnuts
- Benefits of Wheatgrass
- Best Food Fads
- Cacao vs Cocoa
- Caffeine-Free Energy Foods
- Chocolate That's Good for You
- Diet vs. Exercise
- Fat Burning Foods
- Food Myths Debunked
- Foods for Bone Density
- Foods for Colon Health
- Foods for Healthy Hair
- Foods for Healthy Skin
- Foods to Help Sleep
- Foods to Reduce Stress
- Green Tea Benefits
- Healthy Baking Flours
- Heart Healthy Habits
- High Protein Health Risks
- How to Boost Your Metabolism
- How to Lose Weight While Aging
- How to Throw a Vegan BBQ
- Kaniwa vs Quinoa
- Little Health Foods
- Low-Carb: Fad or Friend?
- Making Healthier Desserts
- Mediterranean Diet Meal Plan
- Natural Beauty Products
- Nuts for Weight Loss
- Preparing Vegan Meals
- Preventing Muscle Degeneration
- Rare Superfoods
- Reduce Sugar Intake
- Save Time By Going Vegan
- Smarter Snack Swaps
- Smoothie Ingredients
- Soy Protein vs Whey Protein
- Starting a Plant-Based Diet
- Steel Cut vs Rolled Oats
- Sugar Substitutes
- Vegan Proteins
- Vegan Substitutions for Fall Recipes
- Why Go Vegan
- Healthy Meals
- Healthy Recipes
- Sports Nutrition
- Nutrition and Special Diets
- 21 Day Fix
- 5 Popular Diet Similarities
- Alkaline Diet
- Anti-Inflammatory Diet
- Calorie Counting
- Carb Cycling Diet
- Celiac Disease
- Cholesterol
- Clean Eating
- Crohn's Disease
- DASH Diet
- Detox Diet
- Diabetes
- Diabetes Diet
- Diet Pill Dangers
- Fat Burning Foods
- Gluten-free Diet
- Glycemic Index
- Heart Health
- High Blood Pressure Diet
- High Fiber Foods
- How to Eat Healthy
- How to Lower Blood Pressure
- Hypertension
- IBS Diet
- Ketogenic Diet
- Liquid Diet
- Low GI Foods
- Low-Carb Diet and Foods
- Low-Fat High-Carb Diet
- Mediterranean Diet
- Mediterranean Diet Foods
- Military Diet
- Nutrition Labels Explained
- Paleo Diet
- Raw Food Diet
- Superfoods
- Sustainable Weight Loss
- Thrive Diet
- Vegan Diet
- Vegetarian Diet
- Weight Loss Shakes
- Whole30
- Vitamins, Minerals & Nutrients